简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
SaracenMarkets Account Types & Fees: Pro vs. VIP
Abstract:Compare SaracenMarkets' Pro and VIP account types. Learn about minimum deposits, spreads, leverage, and commission fees. Find out which account suits your trading needs.
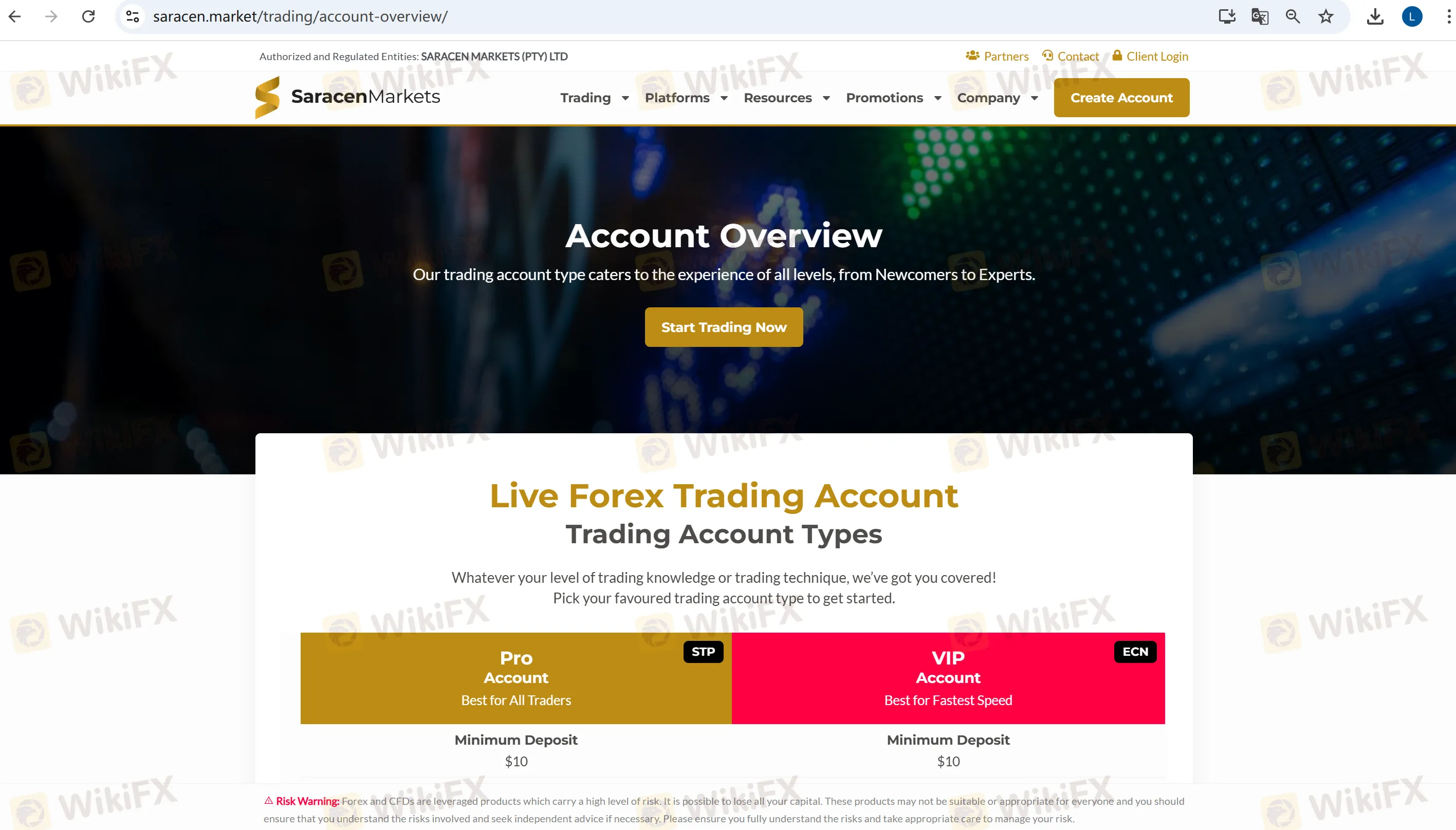
What Account Types Does SaracenMarkets Offer?
SaracenMarkets provides two main account types: the Pro account and the VIP account. The Pro account uses the STP (Straight Through Processing) model with spreads starting from 1.6 pips and no commission. The VIP account uses the ECN (Electronic Communication Network) model with spreads starting from 0.0 pips, but it charges a commission of $5 per lot.
Both account types are available with a minimum deposit of $10, and they offer swap-free Islamic accounts for traders who prefer no overnight interest.
What Are the Differences between SaracenMarkets' Accounts?
| Account Type | Minimum Deposit | Spread | Leverage | Commission | Swap-Free Islamic Account |
| Pro | $10 | From 1.6 pips | 1:2000 | $0 | Yes |
| VIP | $10 | From 0.0 pips | 1:500 | $5 per lot | Yes |
FAQs about SaracenMarkets Account Type & Fees
Q1: What is the minimum deposit for SaracenMarkets accounts?
A1: The minimum deposit for both Pro and VIP accounts is $10.
Q2: What is the spread on SaracenMarkets' Pro and VIP accounts?
A2: The Pro account has a floating spread from 1.6 pips, while the VIP account offers a spread starting from 0.0 pips.
Q3: Does SaracenMarkets charge commission?
A3: The Pro account does not charge commission, while the VIP account charges $5 per lot.
Q4: Can I open a swap-free Islamic account with SaracenMarkets?
A4: Yes, both the Pro and VIP accounts offer swap-free Islamic accounts.
Q5: What leverage does SaracenMarkets offer on its accounts?
A5: The Pro account offers leverage up to 1:2000, and the VIP account offers leverage up to 1:500.
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
MFSA Warns of Digital Market Mining Scam: Alchemy Markets Clone
Alchemy Markets Launches Seamless TradingView Integration
Drawdown in Forex Trading
WikiFX Report: Five Forex Brokers with No Spread
Two Candle Patterns
EC Markets Expands with New Office in Mauritius
What WikiFX Found When It Looked Into CORSA FUTURES
European stocks set to rally at the open as U.S.-Japan trade deal boosts global market sentiment
Just be yourself' is bad advice, says expert—here's what successful people do instead
Opendoor leads meme stock redux on Wall Street with shares tripling in one week
Currency Calculator


